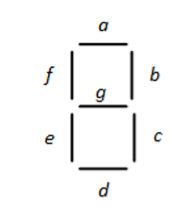Don't Care Terms
Objectives
We would like to :
- Understand why don't care terms exist
- Understand how to deal with don't care terms in K-Maps
Notes
- Carpineli has some information.
- Wikipedia is a good supplement
- The Seven Segment display is a common component.
- 7 or 8 inputs
- a-g drive the lines
- The last one drives the .
-
 (wikipedia)
(wikipedia)
- So there are seven inputs,
- Labeled a-g
-
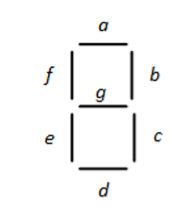
- For the one in Digital, a-d are across the top from left to right.
- e-g are across the bottom left to right
- . is on the bottom far right.
-
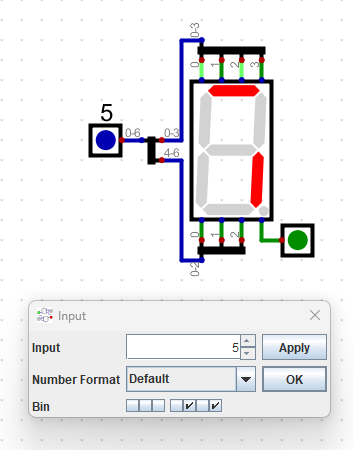
- If we wish to display 0-9
- To display the digits 0 - 9, we need 4 bits.
- Some of the patterns (A16-F16) we don't care about.
- We designate don't cares with an X
- Carpineli gives us this table of logic to light the proper segment when a 4 bit number is input.
-
| b3 |
b2 |
b1 |
b0 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
e |
f |
g |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
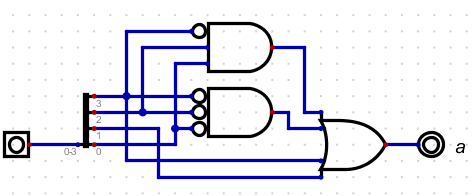
- So if we wanted to build a table for the "a" segment
-
| ab\cd | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 |
|---|
| 00 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
| 01 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
| 11 | X | X | X | X |
|---|
| 10 | 1 | 1 | X | X |
|---|
- When we go to circle in a 4x4 table
- Two rows or two columns represent a single term (8 cells total)
- For terms (one row, one column or a square) represent a two input and
- Two terms represent a 3 input and
- An isolated cell represents a 4 input and.
- Don't cares (x) can be a 0 or a 1, we don't care
-
| ab\cd | 00 | 01 | 11 | 10 |
|---|
| 00 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
| 01 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
| 11 | X | X | X | X |
|---|
| 10 | 1 | 1 | X | X |
|---|
- In this case, all the don't cares were used, but they didn't have to be.
- c
- a
- abd
- a·b·d
- So the function for the a segment is a + c + abd + a·b·d a·b·d
-
- As a side trip, they make BCD to 7-segment decoders/drivers
- We will use the word decoder for something else later.
- The 7448 is such a decoder.
- 4 data inputs, A,B,C,D, A is bit 0, D is bit 3
- 7 data outputs a,b,c,d,e,f,g
- voltage and ground
- lt
- bi/rbo
- bri
- The not lines are normal.
- These are "active" when the value is false.
- lt is the lamp test
- When the lt is low, and BI/RBO goes from low to high, all segments are turned on.
- bi is not blank input.
- If this is low, no segment is lit, regardless of the input.
- bi/rbo acts as a clock, look at the timing diagram on the datasheet.
-
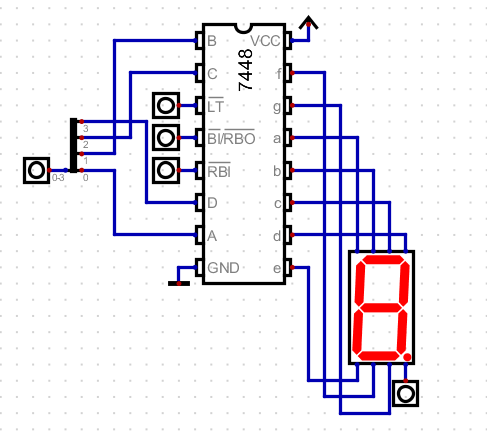
- The digital file
 (wikipedia)
(wikipedia)